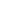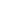32-ports SIM bank refers to a telecommunication device designed to manage and control 32 SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) cards simultaneously. SIM banks are commonly used in various applications to facilitate the remote management of SIM cards, often in the context of GSM/3G/4G/LTE modems or gateways.
Remote and centralized management of SIM cards
No need to switch and recharge SIM cards on-site
Hot swap of SIM cards without powering off the SMB-32/128
Free DDNS service to support dynamic public IP
Management of 32 SIM cards in standalone mode.
Free SIM Server for management of over 10,000 SIM cards
Counter measures for the techniques used for SIM card blocking
Online firmware upgrade
Linux based System
Basic Features
SIM Port: 32 ports
Power Adapter: DC 12V/2A
CPU: ARM9/300MHz
RAM: 32M
Flash: 4M
Max power consumption: 10W
Net weight: 1.34KG
Size:29.2*22.5*5.5cm
Operating Tempreture: 0-45℃
Working Humidity: 10%-90% non condensation
32-ports SIM bank Characteristics
Port Capacity:
The SIM bank supports 32 independent SIM card ports, allowing for the simultaneous management of 32 SIM cards.
SIM Card Slots:
Each port typically has its own SIM card slot, allowing for the insertion and management of individual SIM cards.
Remote Configuration:
Supports remote configuration through a management interface, allowing administrators to update settings and perform tasks without physical access.
API Support:
Some SIM banks provide Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for integration with other systems, enabling automated SIM card management.
Web-Based Management Interface:
Often equipped with a web-based management interface for user-friendly configuration, monitoring, and management.
Security Features:
Implements security features to protect against unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of SIM card management.
Compatibility:
Designed to be compatible with various GSM/3G/4G/LTE modems and gateways, ensuring flexibility in deployment.
Scalability:
Allows for scalability by adding more SIM banks or expanding the number of SIM cards for increased capacity.
SIM Card Management:
Used for remotely managing and controlling multiple SIM cards, enabling operators to perform tasks such as activation, deactivation, and configuration.
GSM/3G/4G/LTE Modems:
Integrated with modems or gateways to provide connectivity to mobile networks for applications such as SMS messaging, data communication, and voice calls.
Bulk SMS Messaging:
Often deployed in scenarios where bulk SMS messaging is required, such as marketing campaigns, notifications, and alerts.
Load Balancing:
Supports load balancing by distributing traffic across multiple SIM cards, preventing overuse of individual cards and optimizing the load on the SIM bank.
Remote SIM Management:
Facilitates remote management of SIM cards, allowing administrators to control and configure SIM cards without physical access to the devices.
Network Redundancy:
Contributes to network redundancy by managing multiple SIM cards, ensuring continuous operation in case of network issues or failures.
VoIP Integration:
Integrated with Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems, enabling the use of SIM cards for voice communication over the internet.